This piece is a assessment on what is occurring in growing manufacturing capability for pc, digital, and electrical manufacturing. The place I’m, there’s growing builds of services for every of these merchandise. That being across the Phoenix space. One facility they’ve been engaged on for 2 years now and it seems to be close to the top. A lot of that is automated and possibly a lot Labor. Semiconductor is principally rising wafer, populated the slices, and layering. I’ve oversimplified it so add to it.
Unpacking the Increase in U.S. Development of Manufacturing Amenities
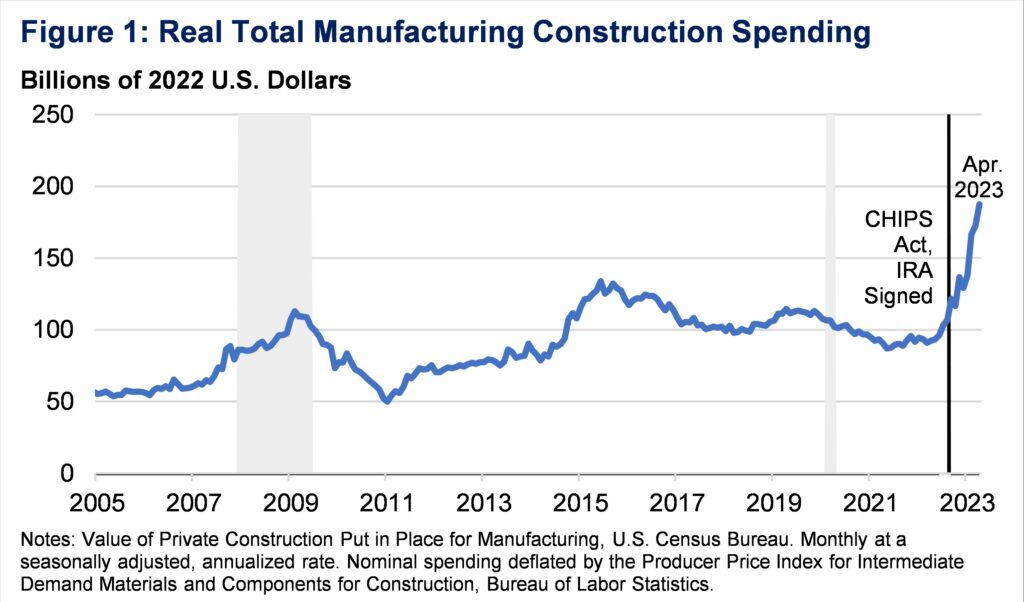
America has skilled a surge in building spending for manufacturing services. Actual manufacturing building spending has doubled for the reason that finish of 2021 (Determine 1). The surge is available in a supportive coverage setting for manufacturing building: the Infrastructure Funding and Jobs Act (IIJA), Inflation Discount Act (IRA), and CHIPS Act every supplied direct funding and tax incentives for private and non-private manufacturing building.
We discover the surge alongside three key dimensions:
- The growth is principally pushed by building for pc, digital, and electrical manufacturing—a comparatively small share of producing building over the previous few many years, however now a dominant element.
- Manufacturing building is one factor of a broader enhance in U.S. non-residential building spending, alongside new constructing for private and non-private infrastructure following the IIJA. The manufacturing surge has not crowded out different forms of building spending, which usually proceed to strengthen.
- Lastly, we put the pattern in worldwide context. Whereas it may be tough to match such granular knowledge throughout nations, the surge seems to be uniquely American and never mirrored in different superior economies.
Decomposing the Surge
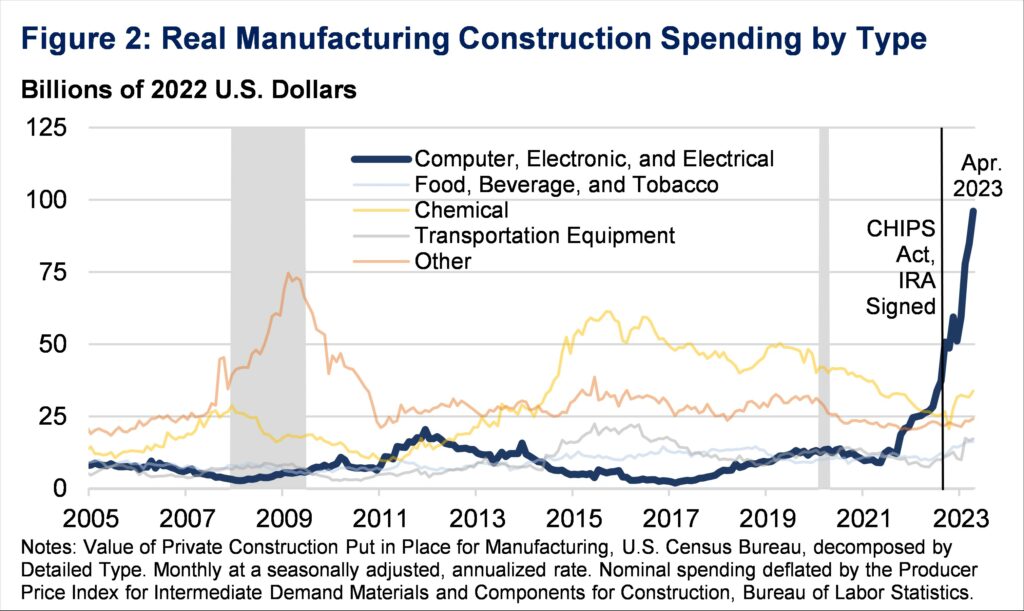
Inside actual building spending on manufacturing, many of the development has been pushed by pc, electronics, and electrical manufacturing. For the reason that starting of 2022, actual spending on building for that particular kind of producing has practically quadrupled (Determine 2).
The adjustment for worth will increase is especially necessary right here. Development prices have risen shortly lately, and due to this fact nominal spending development shouldn’t be misconstrued as elevated bodily building. However by contemplating deflated measures as we do right here, it’s clear that the surge is an actual one (see Appendix for a extra detailed dialogue of our alternative of deflator).
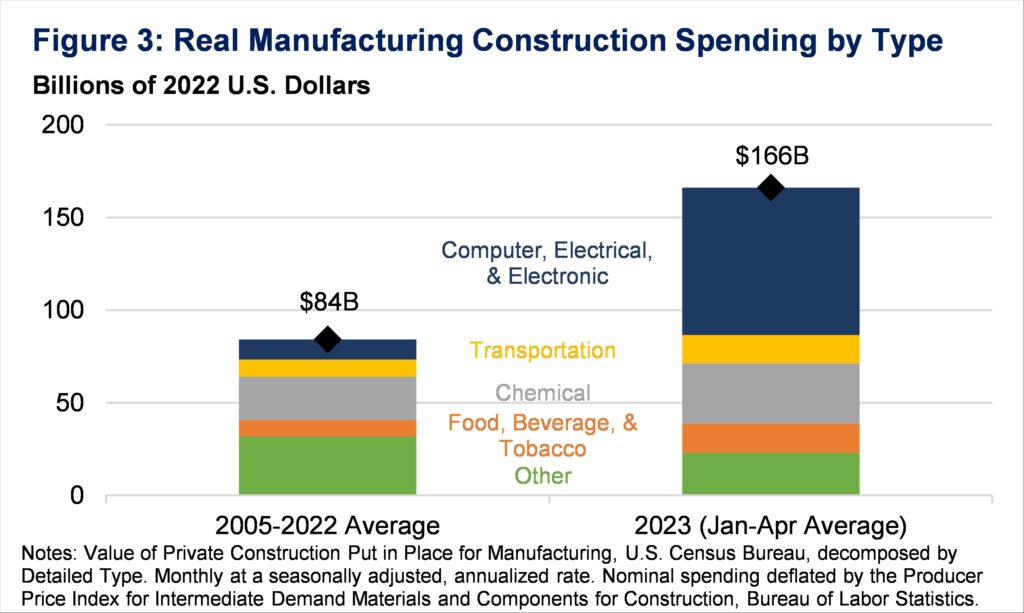
In the present day, the pc/digital section is the dominant element of U.S. manufacturing building. Importantly, the growth on this section has not been offset by decreased spending on different manufacturing building segments, that are largely according to long-term ranges (Determine 3). In truth, building for chemical, transportation, and meals/beverage manufacturing can also be up from 2022, albeit a lot lower than the pc/digital sector.
This rise within the spending started within the months earlier than the CHIPS Act handed, as many components past coverage contribute to building spending. Nonetheless, the laws has performed a crucial half in persevering with and increasing this pattern. Particularly, non-public sector analysts have acknowledged the connection between the expansion in building for electronics manufacturing and the CHIPS Act. Financial institution of America notes this rise got here “potentially on the back of ongoing construction of semiconductor factories as part of the CHIPS Act.” In line with Deutsche Financial institution Analysis, 18 new chipmaking services may have began building between 2021 and 2023. The Semiconductor Business Affiliation studies, over 50 new semiconductor ecosystem initiatives constructed within the wake of the CHIPS Act.
The macroeconomic scenario, coverage implementation, and a variety of different circumstances will proceed to form building manufacturing spending within the months and years to return. Whereas right now’s putting pattern might cool, the CHIPS Act has fostered an ongoing alternative for funding on this sector.
Broader U.S. Non-Residential Development Spending
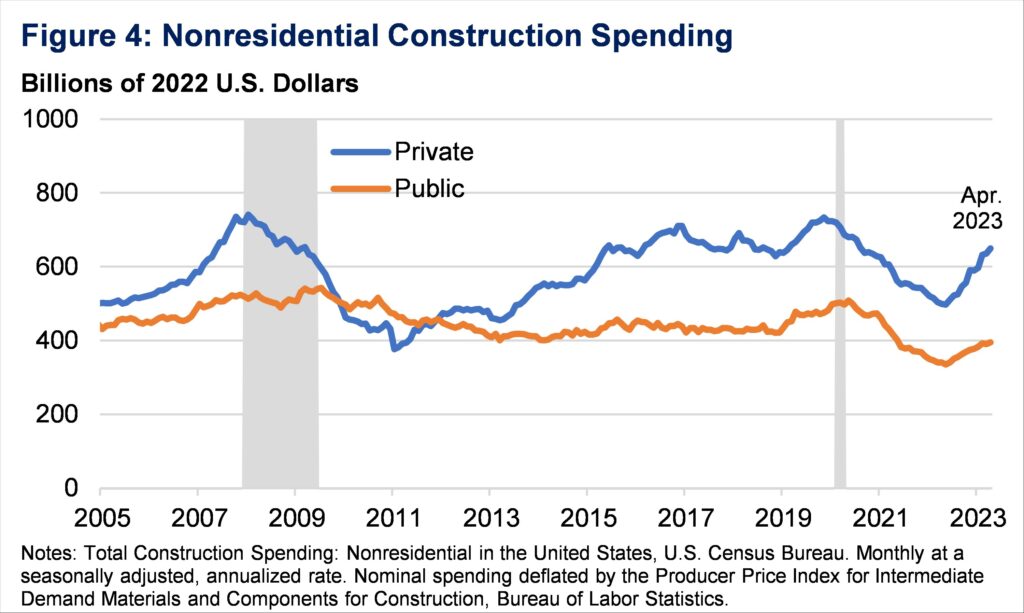
Whereas manufacturing is essentially the most eye-popping element of building spending, total actual nonresidential building spending has elevated by about 15 p.c from November 2021, when the President signed the IIJA, to April 2023. Actual public spending, which elevated by 7 p.c, didn’t crowd out actual non-public spending, which elevated by practically 20 p.c (Determine 4). Furthermore, as extra IIJA initiatives come on-line and break floor, extra private and non-private {dollars} will go towards our public infrastructure.
Beneath the hood, particular elements of building spending, past manufacturing, have additionally had substantial will increase pushed by latest laws. The IIJA licensed the federal authorities to distribute new funds to state and native governments for infrastructure wants tied to roads, bridges, public transit, water, and broadband. That funding has began translating to spending.
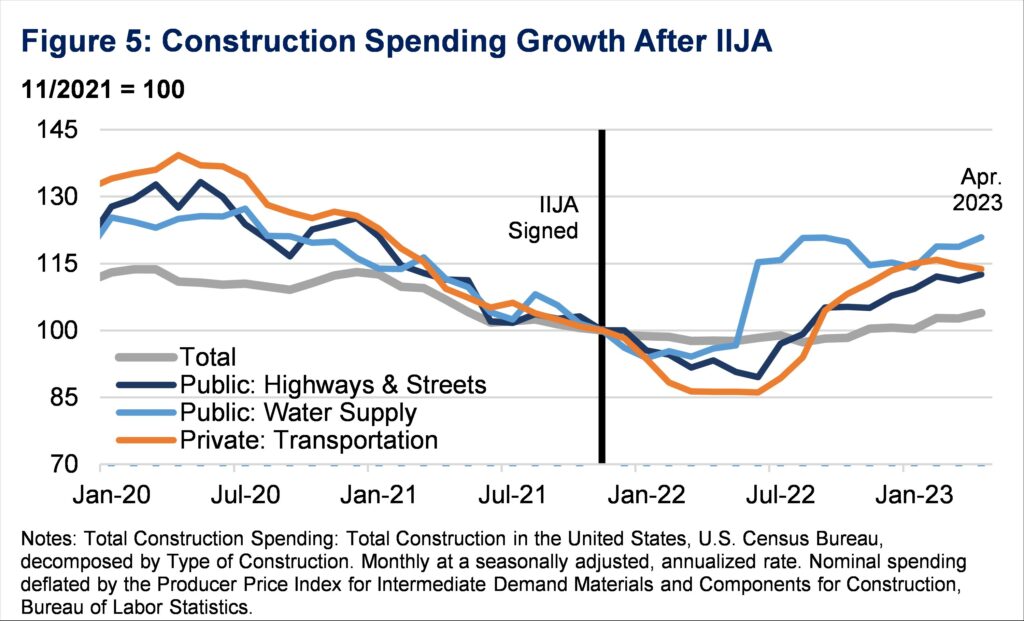
For the reason that invoice’s passage, building spending on these areas has outpaced whole building spending. For instance, whole building spending has elevated about 4 p.c, whereas public building spending on the water provide has elevated by over 20 p.c (Determine 5). The IIJA delivered greater than $50 billion to the EPA to enhance the nation’s ingesting water, wastewater, and stormwater infrastructure. Public spending on highways and streets has additionally elevated by about 13 p.c, because the IIJA funds roads, bridges, and main initiatives with over $110 billion over 5 years.
Once more, the laws elevated public spending however has not crowded out non-public spending. Actual non-public spending on transportation building has grown by practically 14 p.c for the reason that President signed the IIJA. The laws elevated the accessible Non-public Exercise Bonds (PABs) authority from $15 to $30 billion. PABs, allotted by the Secretary of Transportation, incentivize non-public sector funding in U.S. transportation infrastructure. Throughout over 40 initiatives, the Division of Transportation has accredited practically $17 billion and allotted a further $2.8 billion in PABs.
Such investments harness authorities sources to extend productive capability. This being a central aim of Secretary Yellen’s Trendy Provide-Facet Economics coverage framework. Non-public manufacturing for semiconductors, with funding from the CHIPS Act, develop the U.S. economic system’s footprint in a sector important for right now and tomorrow’s applied sciences. Elevated public expenditure on our infrastructure from the IIJA permits a greater functioning, extra resilient economic system. Tax incentives from the IRA tackle the traditionally neglected market failure of local weather change, ushering in a inexperienced power transition that steers the nation towards sustainable development. Every of those initiatives addresses market failures to extend inputs to manufacturing which fuels long-run development.