Scientists investigating Alzheimer’s illness have made a key breakthrough, figuring out an important mobile mechanism driving the commonest reason behind dementia.
The analysis from the Metropolis College of New York (CUNY) offers a promising goal for drug therapies that might gradual, and presumably reverse, the illness’s growth.
The research, printed in the journal Neuron, highlights microglia—the mind’s main immune cells—and their crucial hyperlink to mobile stress within the mind—each the protecting and dangerous responses related to Alzheimer’s.
Microglia, usually dubbed the mind’s first responders, are actually acknowledged as a big causal cell sort in Alzheimer’s pathology. Nonetheless, these cells play a double-edged function: some shield mind well being, whereas others worsen neuro-degeneration.
“We set out to answer what are the harmful microglia in Alzheimer’s disease and how can we therapeutically target them,” stated Pinar Ayata, the research’s principal investigator and a professor with CUNY’s neuroscience initiative inside its Superior Science Analysis Heart.
His workforce pinpointed a “novel neurodegenerative microglia phenotype” in Alzheimer’s illness characterised by a stress-related signaling pathway.
Activation of this stress pathway, often known as the built-in stress response (ISR), prompts microglia to provide and launch poisonous lipids. These lipids injury neurons and oligodendrocyte progenitor cells—two cell varieties important for mind perform and most impacted in Alzheimer’s illness.
Blocking this stress response or the lipid synthesis pathway reversed signs of Alzheimer’s illness in preclinical fashions.
DEMENTIA PREVENTION: Excessive Ranges of Bodily Health Linked to Decrease Dementia Threat in These with Genetic Predisposition
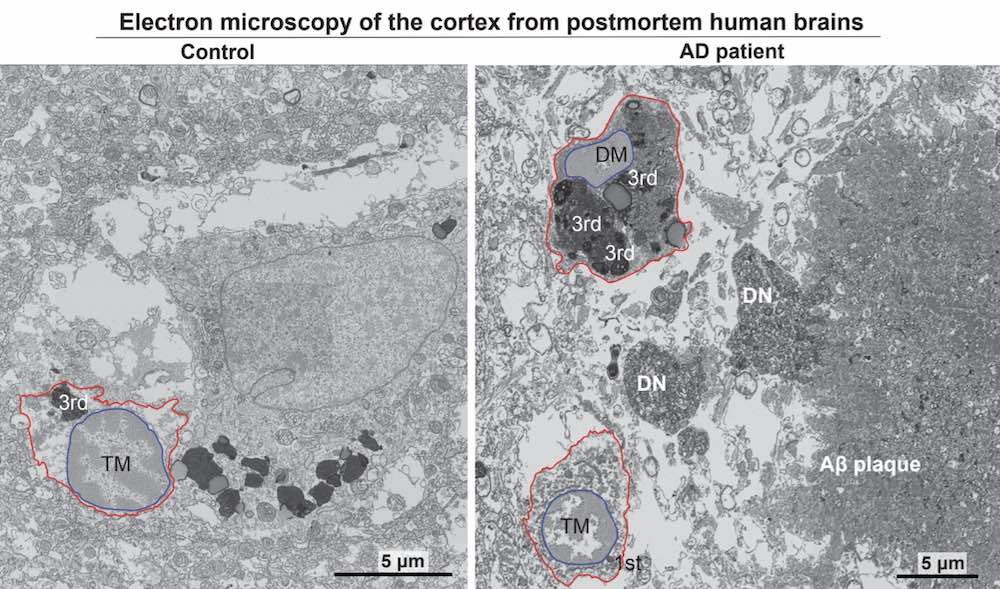
Utilizing electron microscopy, the analysis workforce recognized an accumulation of “dark microglia”, a subset of microglia related to mobile stress and neuro-degeneration, in postmortem mind tissues from Alzheimer’s sufferers.
The cells have been current at twice the degrees seen in healthy-aged folks.
“These findings reveal a critical link between cellular stress and the neurotoxic effects of microglia in Alzheimer’s disease,” stated research co-lead writer Anna Flury.
Ms. Flury, a member of Prof. Ayata’s lab and a Ph.D. scholar, says, “Targeting this pathway may open up new avenues for treatment by either halting the toxic lipid production or preventing the activation of harmful microglial phenotypes.”
The workforce’s research highlights the potential of creating medicine that concentrate on particular microglial populations or their stress-induced mechanisms.
STRESS REDUCTION IN BRAIN? Examine Hyperlinks Leisure Hashish Use to Decrease Threat of Cognitive Decline and Dementia-Associated Ailments
“Such treatments could significantly slow or even reverse the progression of Alzheimer’s disease, offering hope to millions of patients and their families,” concluded co-lead writer Leen Aljayousi, a member of Prof Ayata’s lab.
SHARE THE HOPE By Posting The Staff’s Findings On Social Media…




