I discovered this report on Well being Affairs a day or so in the past. It was lengthy and I spent the final two days condensing it so it might be introduced and skim on Indignant Bear. The authors detailed 4 foremost costs consisting of a Listing Worth, an Out-of-Pocket Worth, insurer’s accountability, and the negotiated worth as soon as all rebates are accounted. Exhibit 1 is a quicky studied to know how the authors arrived on the breakdown. Additionally detailed is the rise in pricing damaged down by these components.
Lastly discovered one thing which provides a greater description of pharma pricing by entity.
Client Out-Of-Pocket Drug Costs Grew Quicker Than Costs Confronted by Insurers After Accounting for Rebates, 2007–20, Well being Affairs
Summary:
This text investigates the complexities of pharmaceutical pricing, with an emphasis on the missed points of producer rebates and out-of-pocket costs. Rebates granted by pharmaceutical producers to insurers scale back the precise costs paid by insurers, inflicting the true costs of prescriptions to diverge from official statistics. The authors mix claims information on branded retail pharmaceuticals with estimates on rebates to supply new worth index measures based mostly on pharmacy costs, negotiated costs (after rebates), and out-of-pocket costs for the commercially insured inhabitants throughout the interval 2007–20.
What was discovered? Though retail pharmacy costs elevated 9.1 p.c yearly, negotiated costs grew by a mere 4.3 p.c, highlighting the significance of rebates in worth measurement. Surprisingly, shopper out-of-pocket costs diverged from negotiated costs after 2016, rising 5.8 p.c yearly whereas negotiated costs remained flat. The priority over drug worth inflation is extra reflective of the fast enhance in shopper out-of-pocket bills than the stagnated inflation of negotiated costs paid by insurers after 2016.
A 2023 KFF survey reported; eight in ten individuals within the US discovered the prices of pharmaceuticals to be unreasonable. Three in ten admitted to prescription nonadherence due to excessive prices.1 Latest authorities interventions, such because the Inflation Discount Act of 2022 and an ongoing investigation by the Federal Commerce Fee,2 search to deal with rising pharmaceutical costs.
The complexity and lack of transparency in pharmaceutical pricing make it troublesome to discern the true prices of medicine.
- One complicating issue is producer rebates, that are reductions on prescription listing costs offered by drug producers to pharmacy profit managers, which in flip could share some or all the rebates with insurers. Extra exactly, pharmacy profit managers negotiate drug costs with drug producers on behalf of insurers. In trade for reductions, pharmacy profit managers grant extra favorable placement on their drug formularies and steer shoppers towards formulary medicine. A 2023 report by the Authorities Accountability Workplace (GAO) discovered proof that pharmacy profit managers construction Medicare Half D formulary tiers to direct gross sales to medicine with comparatively excessive rebates and excessive listing costs which have a decrease web price for the plan sponsor, however not essentially for sufferers.3 Worth transparency is proscribed as a result of non-public nature of those contracts, making it difficult for researchers and authorities companies to evaluate the results of rebates on costs.
- Rebates are paid to pharmacy profit managers after buy. Rebates will not be publicly reported and will not be mirrored within the official statistics from the Bureau of Labor Statistics or the Bureau of Financial Evaluation, that are based mostly on transaction costs at pharmacies (the mixed funds of the insurer and shopper on the time of buy).4,5 This differs with how costs are measured in official statistics for different well being care sectors measuring precise negotiated costs between insurers and medical suppliers.6 The variations imply the important thing measures of pharmaceutical costs used to tell coverage makers and the general public won’t precisely replicate the ultimate price of medicine.
- Additional obscuring measurements of drug costs is neither pharmacy costs nor the negotiated costs replicate what shoppers pay out of pocket on the pharmacy. Privately insured individuals’s copayments, coinsurance, and deductibles are set on the idea of rising pharmacy costs which may not mirror the costs negotiated by insurers. Understanding traits in out-of-pocket costs is especially necessary for 2 causes:
- First, it could generate diverging impressions of worth traits if shoppers’ out-of-pocket costs deviate from insurers’ negotiated costs, and
- Second, there are distributional penalties if out-of-pocket costs are rising shortly, as lower-income populations are disproportionately burdened by these funds. Within the KFF survey, three in ten respondents discovered it troublesome to afford pharmaceuticals, however this rose to virtually 4 in ten amongst households with incomes beneath $40,000.
- The target of this research is to boost public understanding of worth traits within the branded prescription drug marketplace for the commercially insured inhabitants youthful than age sixty-five. We mixed intensive information from non-public prescription drug claims with estimates of rebates. The research lined retail pharmaceuticals from the interval 2007–20 and utilized a constant methodology to measure pharmacy costs, negotiated costs after rebates, and out-of-pocket costs paid by shoppers.
Evaluation
With these information sources, we constructed 4 foremost costs.
- The primary was pharmacy listing worth. The quantity paid to the pharmacy (for instance, CVS, Walgreens and so forth.) for a prescription (suppose $100). The price of the pharmacy listing worth is shared between the affected person and the insurer. Every social gathering is answerable for their share of the pharmacy worth.
- Secondly is the out-of-pocket worth. The quantity the affected person is answerable for paying on the pharmacy (suppose $40). Mathematically, the out-of-pocket worth is the sum of a affected person’s copays, coinsurance, and deductibles towards the prescription.
- After the affected person’s out-of-pocket cost, the remaining stability ($60) is the insurer’s accountability. As a result of insurers obtain confidential rebates (suppose $10), the true worth paid by the insurer was our third worth, the post-rebate insurer worth ($60 − $10 = $50).
- The ultimate worth or the negotiated worth, is the quantity really paid for a drug as soon as rebates have been accounted for ($40 + [$60 − $10] = $90).
Within the research, the pharmacy listing worth and the out-of-pocket worth have been obtained from MarketScan claims. The negotiated worth was constructed by combining SSR Well being information with MarketScan pharmacy worth information. The insurer worth is the negotiated worth minus the out-of-pocket worth paid by shoppers, reflecting the truth that as shoppers pay extra, the insurer pays much less.
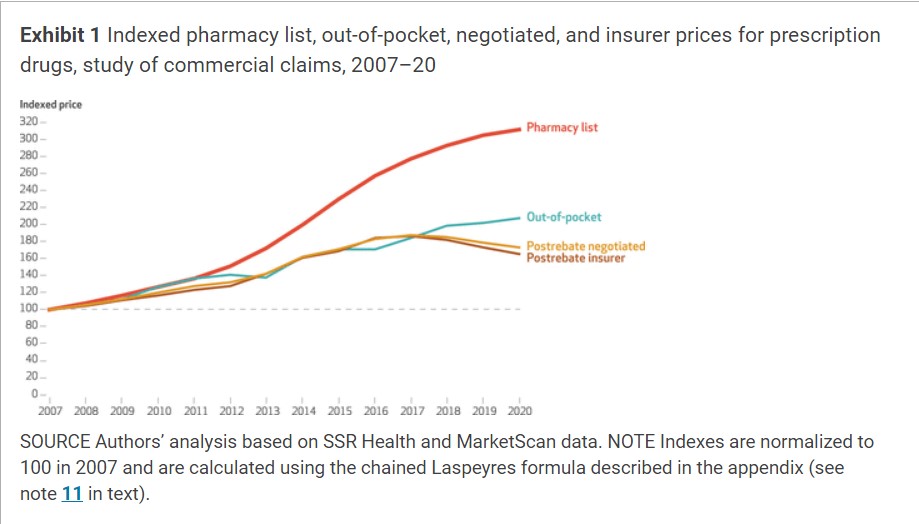
Exhibit 1 illustrates worth inflation throughout our 4 completely different measures of costs. Pharmacy listing costs skilled a mean annual development fee of 9.1 p.c throughout the interval 2007–20. Nevertheless, after adjusting for rebates, negotiated costs grew 4.3 p.c yearly. In distinction, the out-of-pocket worth rose by 5.8 p.c yearly. Progress in insurer costs and negotiated costs intently adopted the expansion in out-of-pocket costs till 2016, when each insurer and negotiated costs started to lower.
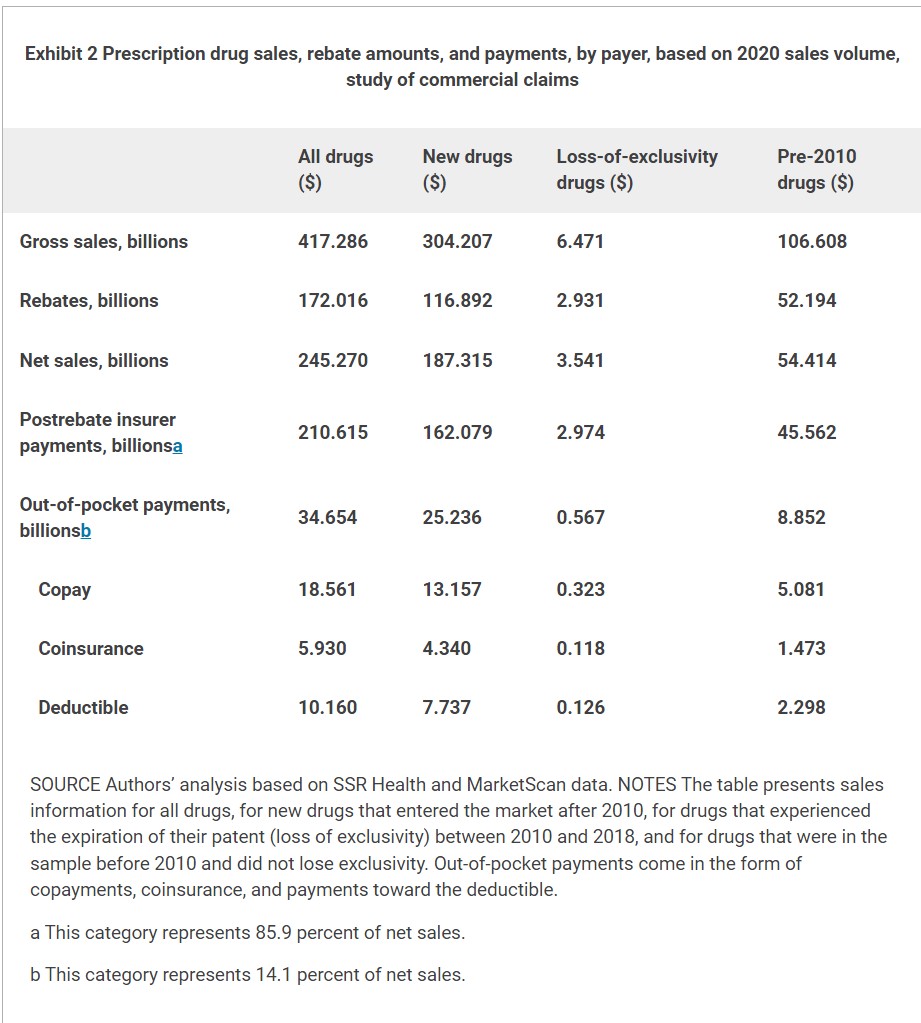
Exhibit 2 exhibits the kinds of medicine driving worth patterns based mostly on 2020 gross sales quantity. The exhibit lists product sales, rebate quantities, web gross sales after rebates, web insurer funds, and web shopper funds. These elements are proven for various teams of medicine: all medicine, new medicine launched after 2010, medicine launched earlier than 2010 shedding their exclusivity earlier than 2018, and medicines launched earlier than 2010 that didn’t expertise a lack of exclusivity.
Exhibit 2 demonstrates that regardless of the fast post-2016 development in out-of-pocket costs proven in exhibit 1, out-of-pocket funds constituted a minority share of the entire price in 2020, accounting for 14 p.c of web gross sales. As well as, new medicine made up a lot of the gross sales, accounting for roughly 75 p.c of gross sales by 2020. As a result of our worth indexes have been gross sales weighted, a lot of the worth traits have been pushed by new medicine that entered after 2010.
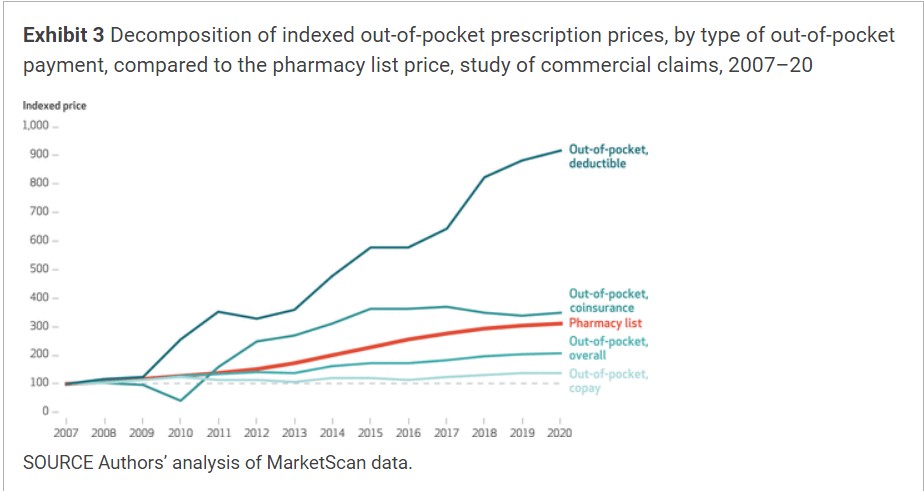
The expansion in out-of-pocket costs deviated from negotiated costs after 2016 (exhibit 1). Whereas Exhibit 3 disentangles which points of the patron funds, deductibles, coinsurance, and copays have been driving the more moderen development in out-of-pocket costs. Progress in total out-of-pocket costs appears to have been pushed by giant will increase in coinsurance and deductible funds. Rising pharmacy costs are more likely to have an effect on deductibles and coinsurance funds, that are sometimes set on the idea of the pharmacy listing worth.
Outcomes of a number of robustness checks have been just like the findings in our foremost evaluation (see appendix reveals A6, A7, A9, and A10).11
Dialogue
The findings have necessary implications for financial measurement and coverage discussions. The research highlights the affect of rebates on measured inflation for branded pharmaceuticals. Rebates will not be presently mirrored in official statistics.
Between 2016 and 2020, out-of-pocket costs skilled quicker development than costs confronted by insurers, after industrial rebates have been accounted for. Considerations about worth development align extra intently with the persistent enhance in out-of-pocket costs than the just lately stagnating development in negotiated costs. The divergence in costs after 2016 raises issues concerning the disconnect between exterior estimates of negotiated costs and the precise prices borne by shoppers. These outcomes are in keeping with the excessive price sharing reported by the GAO,3 in addition to an evaluation by Kai Yeung and colleagues.9 It suggests that refunds can result in a rising hole between negotiated costs and out-of-pocket costs, as rebates drive down negotiated costs whereas growing pharmacy costs drive up out-of-pocket costs. We show these patterns have prolonged to commercially insured People.
New medicine make up the vast majority of the marketplace for branded medicine and have excessive listing costs and excessive rebates that proceed to develop over time. Shoppers are working in an progressive and increasing pharmaceutical market the place they’re spending extra on new medicine and dealing with rising out-of-pocket bills based mostly on much less clear costs as rebates swell.
Our findings on drug worth inflation are complementary to outcomes reported by Pragya Kakani and coauthors8 and Inmaculada Hernandez and colleagues7 demonstrating that rising listing costs don’t translate to larger web funds to producers. We too concluded that after-rebate negotiated funds stagnated after 2016. Rising listing costs do have an effect on shoppers. Our discovering that costs for out-of-pocket funds within the industrial insurance coverage market grew extra shortly than negotiated funds enhances the GAO’s findings that for a lot of medicine, Medicare beneficiaries are paying extra out of pocket than insurers are paying, web of rebates.3
We discovered the growing out-of-pocket bills arose from growing deductible and coinsurance funds. This suggests shoppers will expertise a heterogeneous price burden, relying on their drug plan’s formulary construction. Though shoppers with excessive deductibles or coinsurance could expertise excessive out-of-pocket spending development, shoppers with a low deductible or capped copays look like shielded from steep pharmacy worth will increase.
Rising out-of-pocket costs can disproportionately have an effect on households with decrease incomes who could choose into high-deductible plans with low premiums, not anticipating larger price sharing on the time of buy. We discovered deductible funds drove rising out-of-pocket spending, so rebate-induced worth distortion could also be particularly burdensome for low-income households. Furthermore, prior analysis has discovered that sufferers with continual illnesses pay extra out of pocket whereas underneath high-deductible well being plans than do their counterparts with low-deductible plans.13 Rising rebates and listing costs could exacerbate the burden of plans with excessive price sharing even additional.
Conclusion
Understanding the dynamics of pharmaceutical pricing requires controlling for the position of rebates and contemplating each negotiated costs paid by insurers and out-of-pocket costs paid by shoppers. The research contributes to the literature by combining complete claims and rebate information sources to analyze worth traits amongst key stakeholders within the pharmaceutical provide chain.
Total, the findings emphasize the significance of correct measurement to tell coverage discussions relating to costs in prescription drug markets. Statistical companies such because the Bureau of Financial Evaluation and the Bureau of Labor Statistics have been engaged on this subject. The Bureau of Financial Evaluation, for example, has begun to combine rebates in experimental disease-based statistics.14 Nevertheless, rebates haven’t been accounted for in official inflation measures. Given the information limitations, extra work is required to supply an entire and correct image of how pharmaceutical costs are altering on this sector of rising financial significance.
Client Out-Of-Pocket Drug Costs Grew Quicker Than Costs Confronted By Insurers After Accounting For Rebates, 2007–20 | Well being Affairs, Justine Mallatt, Abe Dunn, and Lasanthi Fernando
Public Opinion on Prescription Medication and Their Costs | KFF